Navigating the Post-Pandemic Real Estate Market
- October 26, 2023
- Posted by: Dre B.
- Categories: Lien And Title Search, Property Records, Property Records Search, Property Title Search, Public Property Records, Real Estate, Real Estate Post, Title Companies, Title Reports
How have homebuyer preferences evolved in the post-pandemic era?
The pandemic has created a surge in demand for all home prices across the U.S. As more people seek a more laid-back work schedule we see our they have realized the importance of having a space where they can work on their own business or career. The convenience of working from home has changed the priorities that home buyers have. Now the priority consists of having a home office when buying a house. Having an office has many advantages like having a quiet and secluded work area. This creates a separation from personal and work life, which a lot of couples these days are seeking out.
How has the supply and demand of housing inventory changed post-pandemic?
- Increased Demand for Larger Homes: The pandemic prompted a shift in housing preferences, with many people seeking larger homes to accommodate remote work, homeschooling, and other lifestyle changes. This led to increased demand for single-family homes, particularly in suburban and rural areas, and decreased demand for apartments and urban living.
- Low Mortgage Rates: Mortgage rates dropped to historic lows during the pandemic, making homeownership more affordable for many. This further fueled demand, as people looked to take advantage of these favorable financing conditions.
- Remote Work and Migration: The rise of remote work allowed people to move away from high-cost urban centers, which had a ripple effect on the housing market. This led to increased demand for homes in areas that were previously less sought after.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: The pandemic disrupted supply chains and construction, leading to delays in home building and renovations. This contributed to a shortage of housing inventory, especially in new construction.
- Rising Home Prices: The combination of increased demand and limited supply led to rising home prices in many areas, creating affordability challenges for first-time homebuyers.
Are we experiencing a buyer’s or seller’s market, and what are the implications?
The housing market in various parts of the United States was primarily a seller’s market. This means that there was a higher demand for homes compared to the supply available.
Sellers Market
- Competitive Bidding: Multiple buyers might be interested in the same property, leading to bidding wars. This can drive prices even higher and make it challenging for buyers to secure a home.
- Quick Sales: Homes tend to sell quickly in a seller’s market, which can be advantageous for sellers looking for a fast sale.
- Limited Negotiation Power for Buyers: Buyers may have limited negotiating power when it comes to price concessions or repairs. They may need to make strong offers to compete with other buyers.
- Frustration for Buyers: Buyers may become frustrated with the competitive nature of the market and may need to act swiftly to secure a property.Buyer’s Market
- Lower Prices: In a buyer’s market, there is an oversupply of homes, which can lead to price reductions. Sellers may need to be more flexible on pricing to attract buyers.
- Negotiation Power for Buyers: Buyers often have more negotiation power in a buyer’s market. They can ask for repairs, concessions, and price reductions.
- Less Competitive Bidding: In a buyer’s market, there are fewer competing buyers for each property, leading to less pressure to engage in bidding wars.
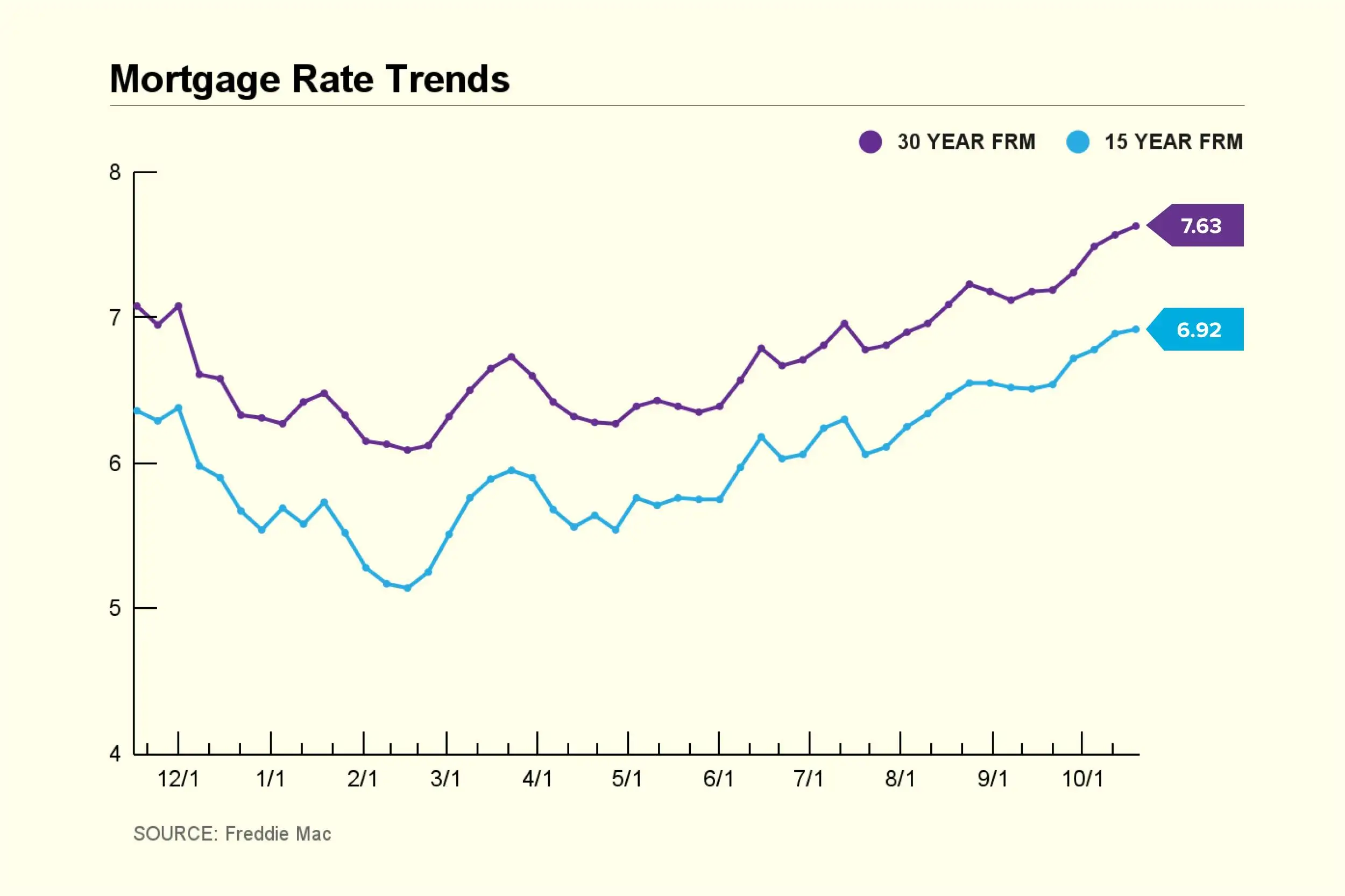
What is the current state of mortgage rates, and how have they fluctuated recently?
The current rate for a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage is 7.63%, an increase of 0.06 percentage points over the past seven days. Last year, the 30-year rate averaged 6.94%.
How have government policies influenced mortgage lending and affordability?
Government policies play a significant role in influencing mortgage lending and housing affordability. These policies are designed to promote homeownership, ensure the stability of the housing market, and protect consumers. Here are some ways in which government policies have influenced mortgage lending and affordability:
- Interest Rates and Monetary Policy:
- Central banks, like the Federal Reserve in the United States, set interest rates, which have a significant impact on mortgage lending. Lower interest rates can make borrowing more affordable and stimulate demand for housing.
- The central bank’s monetary policy, which includes adjusting interest rates, can influence the overall economy and, consequently, the ability of individuals to afford mortgages.
- Down Payment Requirements:
- Government policies often set minimum down payment requirements for obtaining a mortgage. Lower down payment requirements can make homeownership more accessible, especially for first-time buyers.
- Mortgage Insurance:
- Many governments offer mortgage insurance programs that encourage lenders to provide mortgages to borrowers with smaller down payments or lower credit scores. This reduces the risk to lenders, making it easier for borrowers to access credit.
- Loan Guarantee Programs:
- Some governments, such as the U.S. government through the Federal Housing Administration (FHA) and the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), guarantee certain mortgage loans. This reduces lender risk and can lead to lower interest rates and easier qualification for borrowers.
- Tax Incentives:
- Governments may provide tax incentives to encourage homeownership, such as deductions for mortgage interest payments or property taxes. These incentives can make homeownership more affordable.
Navigating the Competitive Landscape
How can buyers and sellers compete effectively in a potentially competitive market?
In a potentially competitive real estate market, both buyers and sellers can take various steps to compete effectively. The strategies they employ will differ based on their roles, but here are some tips for both:
For Buyers:
- Get Pre-Approved for a Mortgage: Before starting your home search, get pre-approved for a mortgage. This shows sellers that you are a serious buyer and that you have the financial means to purchase the property.
- Work with a Real Estate Agent: A knowledgeable real estate agent can help you navigate the market, identify properties that meet your criteria, and negotiate on your behalf.
- Act Quickly: In a competitive market, properties can get multiple offers within days or even hours of listing. Be prepared to act swiftly when you find a property you like.
- Flexibility in Timing: Be flexible with your closing date, as this can make your offer more attractive to sellers.
- Offer a Competitive Price: While you should be cautious about overpaying, offering a competitive price can increase your chances of winning a bidding war.For Sellers:
- Set the Right Price: Pricing your home competitively from the start can attract more buyers. Overpriced homes can linger on the market.
- Prepare Your Home: Ensure your home is in good condition and has curb appeal. Staging can also make a significant difference in attracting buyers.
- Market Effectively: Work with a real estate agent who has a strong marketing strategy. High-quality photos and online listings can attract more potential buyers.
- Review Offers Carefully: When you receive multiple offers, evaluate each one carefully. Don’t just focus on the highest price; consider other terms and contingencies.
- Negotiate Smartly: Be open to negotiating terms that can make your property more attractive to the buyer without significantly impacting your bottom line.
How can U.S. Title Records assist in ensuring secure real estate transactions?
U.S. Title Records can play a significant role in ensuring secure real estate transactions by providing access to essential information about a property’s history and legal status. Here’s how U.S. Title Records can assist in this process:
- Title Search and Examination: U.S. Title Records maintains a database of property records, including information about the property’s ownership history, liens, encumbrances, and legal descriptions. A title search is typically conducted to identify any issues that might affect the property’s title. This process helps ensure that the seller has a clear and marketable title, which is essential for a secure transaction.
- Title Insurance: Title insurance is often a requirement for real estate transactions. U.S. Title Records provide data used in the underwriting of title insurance policies. Title insurance protects buyers and lenders from financial loss due to unforeseen title defects or disputes.
- Ownership Verification: U.S. Title Records can verify the current and previous owners of the property, helping to establish the legitimacy of the seller and the right to transfer ownership.
- Liens and Encumbrances: Information about any outstanding liens, mortgages, or encumbrances on the property is available in these records. This helps buyers understand any financial obligations associated with the property and ensures that they are addressed during the transaction.
- Legal Descriptions: U.S. Title Records provide accurate legal descriptions of the property, which are crucial for defining the property’s boundaries and avoiding boundary disputes.
- Property History: Access to historical property records can provide insights into past ownership, usage, and any potential issues or disputes that may impact the transaction.